Dual-Domain Triple Contrast for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) methods learn from labeled data within source domain and unlabeled data within target domain, and then perform downstream tasks on target domain. Current methods approach UDA task using domain adaptation or self-supervised learning strategies, while our D2TC leverages contrastive learning to integrate both strategies into a unified framework. D2TC is used to perform cross-dataset skeleton-based action recognition for practice evaluation.
Paper Info
- Title: Dual-Domain Triple Contrast for Cross-Dataset Skeleton-based Action Recognition
- Author(s): Kun Wang, Jiuxin Cao, Jiawei Ge, Chang Liu, Bo Liu
- Conference/Journal Name: ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing Communications and Applications (TOMM)
- Date: 2025
- Link: ACM DL
- GitHub: D2TC
Abstract
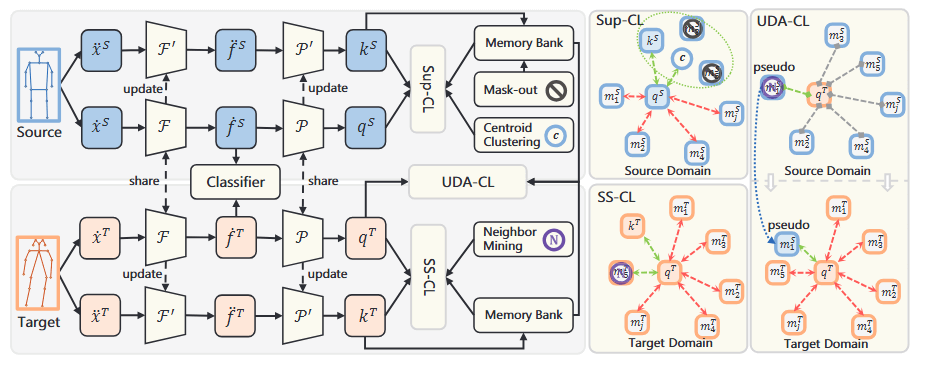
Skeleton-based Action Recognition (SAR) is widely recognized for its robustness and efficiency in human action analysis, but its performance in cross-dataset tasks has been limited due to domain shifts between different datasets. To address this challenge, current methods typically approach cross-dataset SAR as an Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) task, which is tackled using domain adaptation or self-supervised learning strategies. In this paper, we propose a Dual-Domain Triple Contrast (D2TC) framework for cross-dataset SAR under the UDA setting. Unlike existing UDA methods that either focus on a single strategy or superficially combine strategies, our D2TC leverages contrastive learning to integrate both strategies into a unified framework. It performs three types of contrastive learning: Self-Supervised Contrastive Learning (SS-CL), Supervised Contrastive Learning (Sup-CL), and Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Contrastive Learning (UDA-CL), across both source and target domains. The triple contrasts go beyond mere summation, effectively bridging the domain gap and enhancing the model’s representational capacity. Additionally, we introduce multi-modal ensemble contrast and extreme skeleton augmentation methods to further enhance the skeleton-based representation learning. Extensive experiments on six cross-dataset settings validate the superiority of our D2TC framework over state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating its effectiveness in reducing domain discrepancies and improving cross-dataset SAR performance.
Citation
If you find this idea helpful, please consider citing:
@article{10.1145/3715917,
author = {Wang, Kun and Cao, Jiuxin and Ge, Jiawei and Liu, Chang and Liu, Bo},
title = {Dual-Domain Triple Contrast for Cross-Dataset Skeleton-based Action Recognition},
year = {2025},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
issn = {1551-6857},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3715917},
doi = {10.1145/3715917},
note = {Just Accepted},
journal = {ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl.},
month = jan,
keywords = {Skeleton-based action recognition, Unsupervised domain adaptation, Self-supervised learning, Contrastive learning}
}